
Once you have created a table in your document, you may want to spiff it up a bit by changing the borders.
Luckily, it is
not all that difficult to do in Word and there are several methods you
can choose from to accomplish this, which are listed below:
- When you select your table or place your cursor in your table, you will notice that the Conditional Table Tools menu becomes available, where you will see both the Design and Layout tabs. In the Design tab, look in the Table Styles group where you will find the Borders tool.
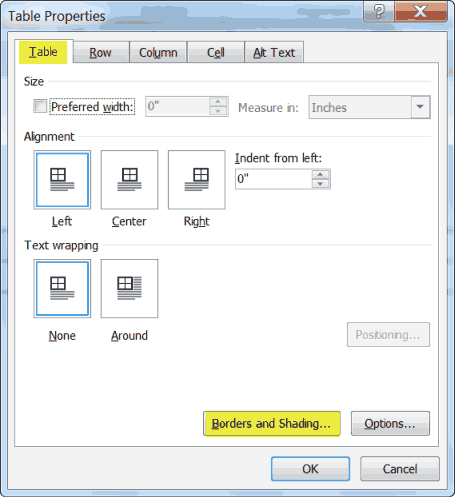
- Under the Layout tab, in the Table group, click on the Properties command and Word will display the Table Properties dialog box, where you will find a Borders and Shading button.
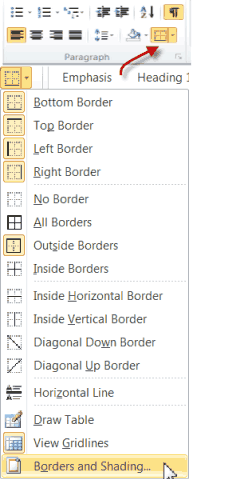
- The Borders control on the Home tab of your ribbon, in the Paragraph group also works on tables.
- There is a Borders and Shading option on the context menu when you right-click in your table.
- The Draw table and Eraser controls found in the Tool’s Design tab, in the Draw Borders group will allow you to add and remove table lines one cell at a time.
If you click on the arrow of any of the various Borders tools, a drop-down list of ways to apply border lines to your whole table and individual cells will appear.
If borders have been applied to to the table cell where your cursor is, as in gridlines, the Borders control will be highlighted.
Interestingly
enough, if your current cell does not have a border applied, but there
are borders applied to any cell in your table then, at least one of the
lines in the table in the borders control icon in your ribbon will be
solid. It does not really stand out, so you will have to look closely to
see it.
At the very bottom of the Borders drop-down list there are options to display the Borders and Shading dialog box and to toggle View Gridlines.
The Draw Table and Eraser tools are great for adding and removing one or two lines at specific locations in your table. The Draw Borders group can be found on the Design tab and it is the last one. It contains controls to set line thickness, color and style.
Clicking the Draw Table tool will convert your cursor to a pencil. Thereafter, clicking on any line in your table makes the line the color, style and thickness selected in the tool.
Clicking and dragging between any two lines in your table cell will split the cells along those line.
Clicking on the Eraser tool
changes your cursor into an eraser that will delete any cell lines that
it touches. The Esc key will cancel the eraser mode.
Regardless of
which method you select to create your borders, there are myriad ways in
which you can accomplish this task. Try them all and then make your
decision on what best suits your particular needs.
Courtesy : http://bnjho.blogspot.in/






